Overview
A person’s quality of life can be greatly impacted by pain, which can have an impact on anything from everyday activities to mental health. The management and treatment of pain are essential for regaining function and enhancing general health. This piece will examine several approaches and treatments for pain management with the goal of improving the lives of those who experience either acute or chronic pain.
Comprehending Pain
Gaining insight into the nature of pain is crucial before implementing any pain management techniques. There are two primary types of pain: acute and chronic. Short-lived in nature, acute pain frequently acts as a warning indication that something is amiss in the body. Conversely, chronic pain lasts longer—often for months or even years—than other types of pain. Debilitating effects of chronic pain can be seen in mood, movement, and general quality of life.
The Value of Pain Management
Efficient pain management is essential for enhancing general wellbeing in addition to relieving suffering. Unmanaged pain can result in a number of problems, such as diminished mobility, insomnia, anxiety, and depression. As a result, implementing effective pain management techniques is crucial to improving the quality of life for those who are in pain.
Multimodal Approach to Pain Management
When treating pain, a multimodal approach combines many therapies and techniques to tackle the problem from various perspectives. This strategy can help patients achieve better results because it is frequently more successful than depending just on one technique. The following are essential elements of a multimodal pain management program:
Medication Management:
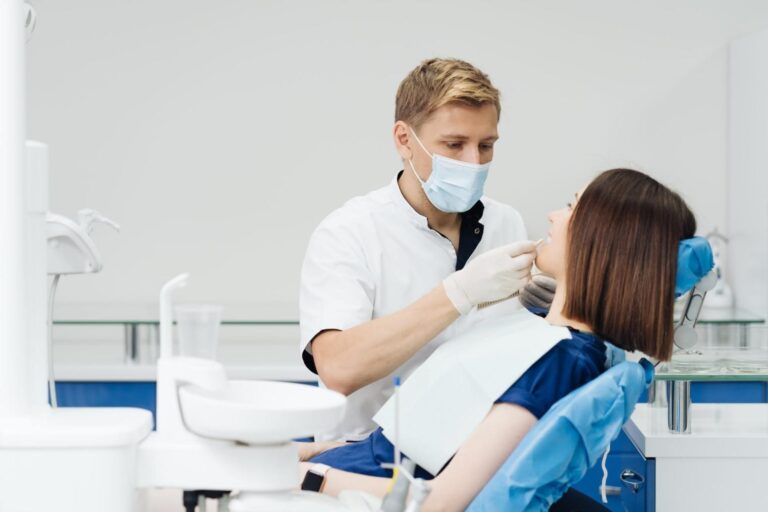
The mainstay of pain management is frequently medication. Pain management often involves the prescription of opioids, muscle relaxants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). To prevent potential adverse effects and dependency, it’s imperative to use these medications sparingly and under a doctor’s supervision.
Physical Therapy: In the case of musculoskeletal disorders in particular, physical therapy is an essential component of pain management. Stretches, manual therapies, and therapeutic exercises can assist increase range of motion, strength, and flexibility while lowering discomfort and improving function.
Mind-Body Methods:
Mind-body methods, such mindfulness training, meditation, and relaxation techniques, can be very effective in treating pain. By lowering stress, elevating mood, and fostering a sense of wellbeing, these methods can lessen pain symptoms without directly causing them.
Alternative Therapies:
A number of non-traditional therapies have demonstrated potential for relieving pain. These consist of massage therapy, chiropractic adjustments, herbal therapies, and acupuncture. Numerous people find these therapies helpful in managing their pain, but additional study is required to completely confirm their usefulness.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
A number of lifestyle aspects, including stress reduction, nutrition, exercise, and sleep hygiene, are important for managing pain. A healthy lifestyle can help manage pain in addition to other pain management techniques by lowering inflammation and enhancing general health.
Advances in the Management of Pain
Pain management techniques have evolved as a result of breakthroughs in medical technology and study. The goal of these developments is to reduce side effects while delivering more focused and efficient pain management. The following noteworthy advancements in the management of pain:
Neuromodulation:
Neuromodulation methods include electrical impulses used to control the activity of the nervous system. Examples of these methods are peripheral nerve stimulation and spinal cord stimulation. These methods can be useful in the treatment of neuropathic pain and failed back surgery syndrome, two chronic pain syndromes.
Radiofrequency Ablation:
This minimally invasive technique works by interrupting the nerve signals that cause pain by using the heat produced by radio waves. This method is frequently used to treat persistent pain in the joints, nerves, and spine.
Injection of a concentrated amount of platelets from the patient’s blood is the process of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, which is administered to the affected area. This treatment may help with pain reduction, particularly in musculoskeletal disorders, as it is believed to accelerate tissue healing and decrease inflammation.
Cannabinoids:
Derived from the cannabis plant, cannabinoids have drawn interest due to their possible application in the treatment of pain. Two cannabinoids that have been researched for their analgesic qualities are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Some people report significant pain alleviation from cannabinoid-based therapy, but additional research is required.
Psychological Methods for Handling Pain
Psychological techniques are essential for managing pain in addition to physical ones. Anxiety, despair, and mobility phobia are among the emotional distresses that are frequently linked to chronic pain. Enhancing coping strategies and addressing these variables are the goals of psychological therapy. The following psychological techniques are frequently applied in pain management:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy, or CBT, is an organized therapeutic approach that assists patients in recognizing and altering harmful thought patterns and behaviors. CBT can assist people in managing their stress, reducing pain-related impairment, and learning coping mechanisms in the context of pain treatment.
Biofeedback:
Biofeedback methods use sensors to track physiological reactions including skin temperature, muscle tension, and heart rate. People can learn to regulate these reactions through biofeedback training, which may help people feel less discomfort and feel more at ease.
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) is a stress-reduction approach that integrates yoga and mindfulness meditation techniques to enhance awareness of the present moment. This method can help those who are in chronic pain since it promotes acceptance, lowers stress levels, and improves general wellbeing.
Holistic Methods of Treating Pain
The goal of holistic pain management is to treat the patient as a whole, not just their symptoms. These methods consider the mental, emotional, social, and spiritual facets of well-being. Here are a few complementary methods of treating pain:
Nutrition:
Controlling pain and inflammation can be greatly aided by eating a well-balanced and nourishing diet. Foods high in anti-inflammatory substances, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants help improve general health and lessen the sensations of pain.
Sleep hygiene:
Getting a good night’s sleep is crucial for managing pain and feeling well overall. It is possible to enhance sleep quality and lessen the intensity of pain by adopting appropriate sleep hygiene practices, which include keeping a regular sleep schedule, establishing a calming bedtime ritual, and optimizing the sleep environment.
Social Support:
Having a strong support system and social relationships is essential for managing chronic pain. Getting involved with friends, family, support groups, or counseling services can help with coping mechanisms, lessen feelings of loneliness, and offer emotional support.
Complementary Therapies:
Conventional pain management methods can be enhanced by complementary therapies like aromatherapy, music therapy, art therapy, and pet therapy. These treatments encourage emotional expression, stress reduction, and relaxation, all of which can help with pain management and general wellbeing.
In summary
Pain management is a complex process that calls for an all-encompassing strategy that takes into account lifestyle, psychological, and physical aspects. Adopting a multimodal approach can significantly enhance an individual’s overall quality of life and pain alleviation by combining medication management, physical therapy, psychological therapies, and holistic approaches. To improve outcomes and provide people with acute or chronic pain issues hope, more research and innovation in pain treatment are needed.